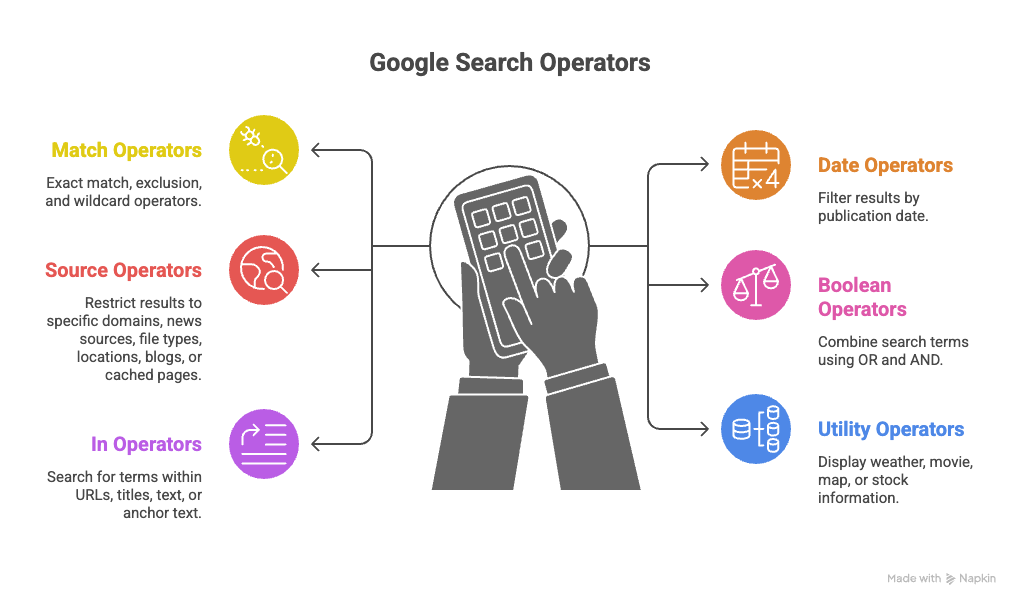
What Are Google Search Operators?
Google search operators are powerful commands that help you filter and refine search results beyond what the standard search box offers.
Think of them as filters that tell Google exactly what you’re looking for. These operators work by instructing Google’s algorithm to include, exclude, or prioritize certain types of content in your search results.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything from the most popular operators like the site operator and filetype commands to advanced combinations that professionals use daily.
Instead of manually combining operators, you can use our Google Search Operator Query Generator to create precise Google queries faster and uncover results most people never see.
Google Search Operators Cheat Sheet 2026
Here’s a quick reference of the top 10 google search operators you should know:
| Operator Purpose Example | ||
site: | Search within a specific website | site:reddit.com productivity |
filetype: | Find specific file formats | filetype:pdf annual report |
intitle: | Search in page titles | intitle:guide python |
inurl: | Search in URLs | inurl:blog marketing |
"exact match" | Find exact phrase | "digital marketing strategy" |
- | Exclude terms | python -snake |
* | Wildcard | best * for beginners |
.. | Number range | laptop $500..$1000 |
OR | Either term | SEO OR SEM |
related: | Similar websites | related:nytimes.com |
Match Operators
"exact match"-exclude operator*asterisk operator
Exact Match Operator
The exact match operator forces Google to return results that include the exact phrase you specify. Normally, if Google cannot find your exact keyword, it shows similar alternatives — this operator prevents that behavior.
Google Search Operators Exclude –
The exclusion operator is used together with keywords or other operators to exclude specific terms from search results, helping you deliberately remove noise from the SERPs. By clearly seeing what is not included, you gain better awareness, discover alternative result sets, and refine intent-focused searches. In practice, the google search operators exclude function uses the minus sign (-) to filter out unwanted results without changing the core meaning of your query.
Examples:
python tutorial -snake marketing -jobs -salary recipe -pinterestYou can exclude:
- Specific words:
-word - Entire sites:
-site:example.com - File types:
-filetype:pdf - Multiple terms:
-word1 -word2 -word3
Google Search Operators Asteriks Or Wildcard *
The asterisk, also known as the wildcard operator, is useful when parts of a phrase are missing or unknown. It can represent any word or phrase
Date Operators
before:after:
The before and after operators let you filter Google search results by publication date. They are especially useful when you want to avoid outdated content or focus only on very recent information.
Before operator
The before: operator returns results published before a specific date.
Syntax:
before:YYYY-MM-DD keywordExample:
before:2020-01-01 SEO strategiesThis shows SEO-related pages published before January 1, 2020, which is useful for historical research or tracking how a topic evolved over time.
After operator
The after: operator returns results published after a specific date.
Syntax:
after:YYYY-MM-DD keywordExample:
after:2024-01-01 Google algorithm updateThis finds content published after January 1, 2024, helping you focus on fresh and up-to-date information.
Using before and after together (date range)
You can combine both operators to search within a specific time range.
Example (date range search):
after:2023-01-01 before:2024-01-01 AI SEO toolsThis returns pages about AI SEO tools published only in 2023.
Using before: and after: together is one of the most effective ways to control result freshness and eliminate outdated or irrelevant pages.
Source Operators
site:source:filetype:loc:blogurl:cache:
Site Operator Google Search
The site operator is arguably the most useful Google search operator. It restricts results to a specific website or domain.
You can use it not only with root domains but also with specific categories or subdirectories to list blog posts under a certain path.site: is one of the most commonly used Google search operators.
It is also very useful for checking the indexation status of your pages in Google.
Basic syntax:
site:example.com keywordExamples:
site:wikipedia.org artificial intelligence– Find all Wikipedia pages about AI
site:edu climate change– Search only educational institutionssite:twitter.com from:elonmusk– Find tweets from a specific account Why the site operator matters: The site search operator is essential for:- Checking what pages Google has indexed from your website
- Competitive research on competitor websites
- Finding specific content on large websites without using their search function
- Discovering guest post opportunities on specific domains
Filetype Search Operator
The filetype operator (also written as filetype google operator) lets you search for specific file formats. This is incredibly useful for finding downloadable resources.
Basic syntax:
filetype:pdf keywordExamples:
filetype:pdf "social media marketing strategy"– Find PDF guides on social mediafiletype:xlsx budget template– Locate Excel spreadsheet templatesfiletype:ppt presentation design– Discover PowerPoint presentationsfiletype:docx resume template– Find Word document templates
Supported file types:
- Documents: pdf, doc, docx, txt, rtf
- Spreadsheets: xls, xlsx, csv
- Presentations: ppt, pptx
- Images: jpg, png, gif, svg
- Others: xml, json, sql
Boolean Operators
OR/|AND
Boolean operators allow you to logically combine multiple search terms and expand or narrow your search results.
Boolean Google Search
Boolean operators aren’t technically Google-specific, but they’re essential for combining search operators effectively. Boolean logic uses AND, OR, and NOT (represented by - in Google) to create complex queries.
Boolean operator examples:
"social media" AND marketingFinds pages containing both terms (Google does this by default).
marketing OR advertisingFinds pages with either term.
marketing -advertisingFinds pages about marketing but excludes those mentioning advertising.
Boolean Google search combinations:
site:edu filetype:pdf "machine learning" -textbookThis finds PDF files on educational sites about machine learning, excluding textbooks.
For patent research, you can use google patent search boolean operators on patents.google.com:
(artificial intelligence OR machine learning) AND autonomous vehiclesIn (URL, Title, Text, Anchor) Operators
inurlandallinurlintitleandallintitleintextandallintextinanchorandallinanchor
Inurl Operator
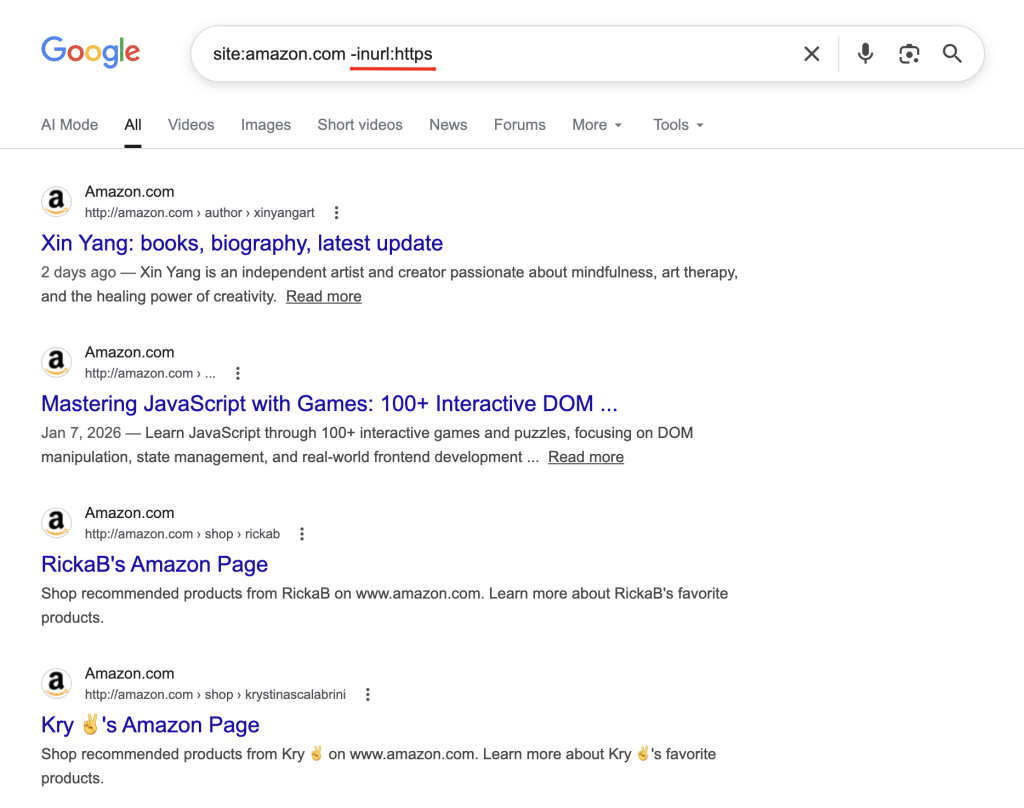
The inurl: operator searches for keywords in the URL.
Examples:
inurl:blog "guest post" inurl:/category/ marketingIntitle and Allintitle Operator
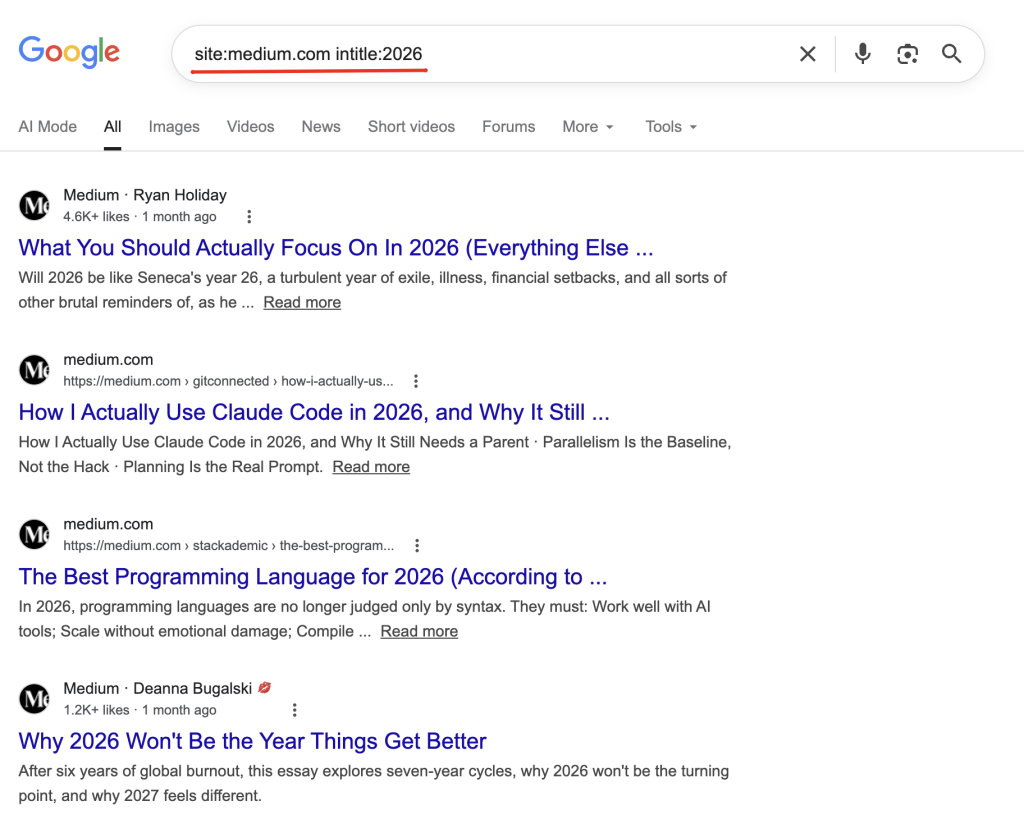
Example:
intitle:("what is"|"what are")The google intitle command searches for keywords in page titles.
Basic syntax:
intitle:keywordExamples:
intitle:"beginner's guide" SEO– Finds pages with “beginner’s guide” in the title and SEO anywhere on the pageallintitle:python tutorial 2026– Finds pages with ALL these words in the title
Key difference:
intitle:– Only the first keyword must be in the titleallintitle:– ALL keywords must be in the title
These operators help you target where keywords appear on a page, making them extremely powerful for SEO research.
Utility Operators
Utility operators are designed for quick informational lookups directly from Google’s search interface. They often trigger Google’s built‑in features or knowledge panels rather than returning traditional blue‑link results.
Other utility‑based operators and commands
While not always documented as formal operators, Google also supports utility‑style searches such as:
related:
Finds websites that Google considers similar to a given domain. This is useful for competitor discovery and market research.
Example: related:nytimes.com
weather:
Displays current weather conditions and forecasts for a specific location directly in the search results.
Example: weather:london
movie:
Shows information about a movie, including showtimes, cast, trailers, and reviews.
Example: movie:Oppenheimer
map:
Opens Google Maps results for a specific place or query, helping with location‑based searches.
Example: map:coffee shops near me
stocks:
Displays real‑time or recent stock market data for a company or ticker symbol.
Example: stocks:GOOGL